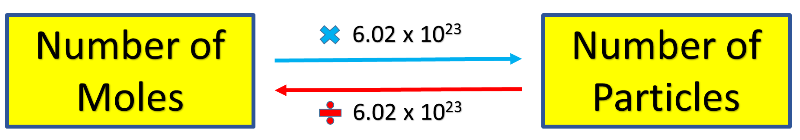
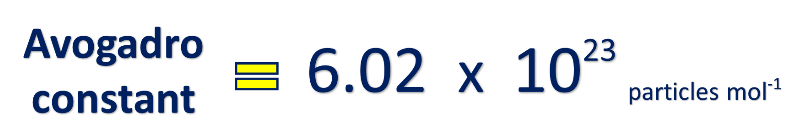Use this formula:

How many formula units are there in 1 mole of sodium chloride?
1 mol NaCl = 6.02 x 1023 NaCl formula units
*1 mole of sodium chloride contains 6.02 x 1023 NaCl formula units.
How many formula units are there in 2 moles of sodium chloride?
2 mol NaCl = 2 x 6.02 x 1023 = 1.204 x 1024 NaCl formula units
*2 moles of sodium chloride contains 1.204 x 1024 NaCl formula units.
How many ions are there in 2 moles of sodium chloride?
2 mol NaCl = 2 x 6.02 x 1023 = 1.204 x 1024 NaCl formula units
2 mol NaCl = 2(2 x 6.02 x 1023)= 2(1.204 x 1024) = 2.408 x 1024 atoms
*2 moles of sodium chloride contains 2.408 x 1024 ions (combination of Na+ ions & Cl– ions).
How many sodium ions are there in 2 moles of sodium chloride?
2 mol NaCl = 2 x 6.02 x 1023 = 1.204 x 1024 NaCl formula units
2 mol NaCl = 1(2 x 6.02 x 1023)= 1(1.204 x 1024) = 1.204 x 1024 Na+ ions
*2 moles of sodium chloride contains 1.204 x 1024 Na+ ions.
How many chloride ions are there in 2 moles of sodium chloride?
2 mol NaCl = 2 x 6.02 x 1023 = 1.204 x 1024 NaCl formula units
2 mol NaCl = 1(2 x 6.02 x 1023)= 1(1.204 x 1024) = 1.204 x 1024 Cl– ions
*2 moles of sodium chloride contains 1.204 x 1024 Cl– ions.
Note: 2 moles of sodium chloride contains 1.204 x 1024 Na+ ions & 1.204 x 1024 Cl– ions. Therefore, the total number of ions in 2 moles of sodium chloride is 2.408 x 1024 ions.
(1.204 x 1024) + (1.204 x 1024) = 2.408 x 1024 ions